Deep-learning-enabled probabilistic inference
Probabilistic machine learning methods are powerful tools for modeling phenomena in science and engineering problems, which opens up interesting ways to guide discovery and exploration. However, it remains very challenging to do inference with these probabilistic models in a scalable yet accurate way. In general there is a trade-off, in order to achieve better scalability, one needs to resort to a simplified model and compromise expressiveness and accuracy.
I am developing methods that greatly improve the scalability of probabilistic models without model simplification, via developing neural model to amortize the computationally expensive procedure in probabilistic inference.
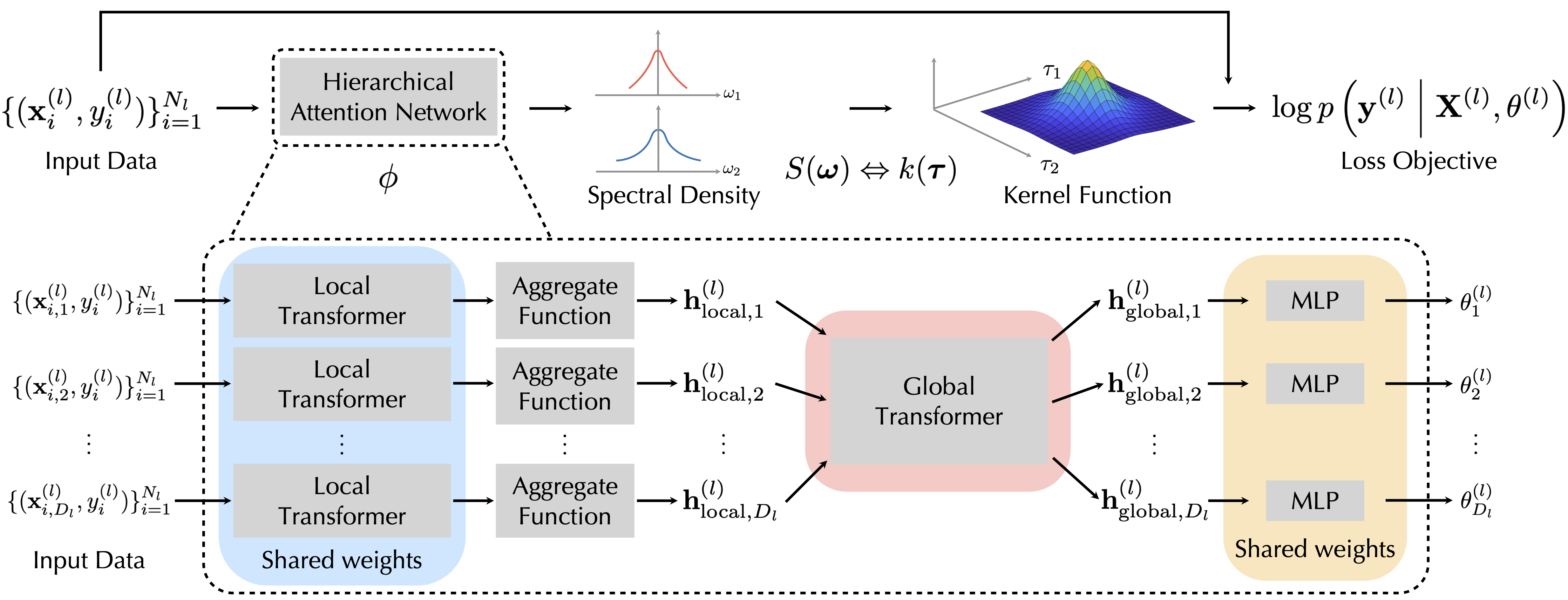
- Speeding up Gaussian process hyperparameter inference (domainating cost of using GPs) by 100$\times$, which can greatly reduce computation invovled in use cases of GP in science and engineering, such as black-box optimization (in drug discovery, chemistry reaction optimization) or Bayes quadrature (estimating intractable integrals).
Related Publications
Task-Agnostic Amortized Inference of Gaussian Process Hyperparameters. Paper
| Code
| Slides
| Video
Sulin Liu, Xingyuan Sun, Peter J. Ramadge, Ryan P. Adams.
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020.
short version at 7th ICML Workshop on Automated Machine Learning. (Spotlight talk)